Work
Note. This section covers only the interesting parts of my past work, not all of it. The projects included here are those where I had meaningful ownership, learned something I care about, or found the problem space particularly engaging. It is not a complete employment history.
Download my resume here.
-
2025–26Model Research and Engineering
Still cooking something here. Proprietary work, so I can't say much yet.
-
2025OxPython: Hardware Agnostic Compiler and Runtime
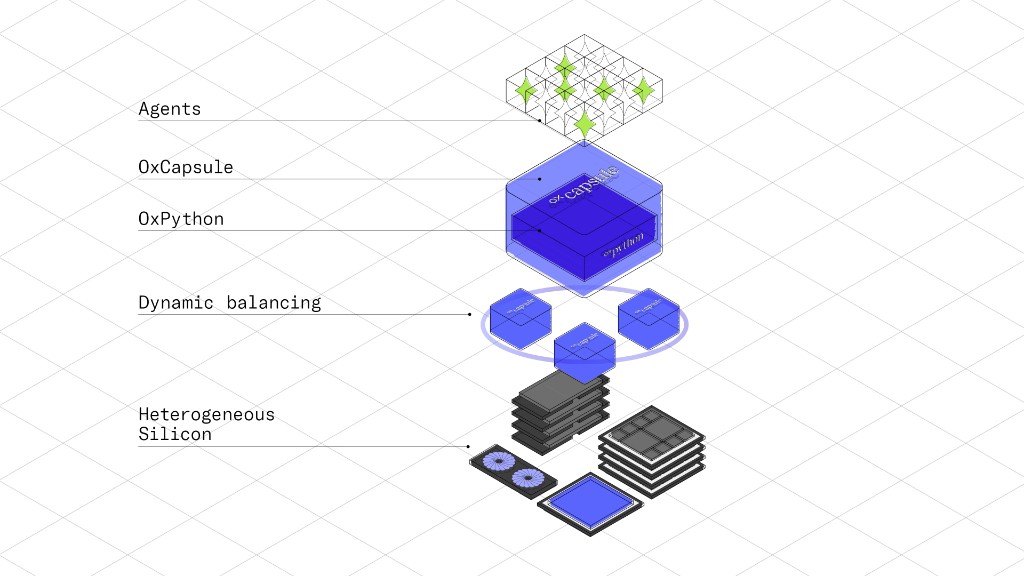
Source: oxmiq.ai Under the vision of Raja Koduri
- Architected a PyTorch compiler that leverages torch.compile and torch-mlir to enable efficient deployment of LLM and diffusion models across heterogeneous hardware.
- Engineered an asynchronous queuing system for torch dispatch that enables efficient execution across heterogeneous hardware.
- Developed an optimized garbage collection system for on-device tensor deallocation in torch's eager execution mode during runtime.
-
2024Hardware Agnostic Performance Optimization and Model Deployment
- Designed algorithms for efficient matrix multiplication tiling for hardware acceleration.
- Researched CUDA and CuBLAS tiling strategies to enhance tensor operation performance.
- Analyzed batching effects in MLP and Attention layers of transformer architectures to optimize inference throughput.
- Evaluated Deepseek_r1_Distil_Qwen_1.5_b and CogVideoX models, creating optimized inference pipelines for deployment.
- Implemented Llama 3.2 1B from scratch with optimizations for deployment across heterogeneous hardware.
Fine-Tuning and Quantization Techniques for Enhanced Efficiency in LLMs for Task-Specific Code GenerationUnder the mentorship of Satya Uppalapati, with guidance from Wajahat Qadeer, Rajashekar Reddy, and Siva Kumar Vemuri. Thesis submitted to BITS Pilani, India.
Deploying Large Language Models on Kinara's Edge AI Processor: Novel Quantization Techniques and Compiler Optimization- Examined systematic outliers across various Language Model architectures (LLMs) to evaluate their suitability for deployment on edge devices, including llama7b (both base and chat versions), qwen7b, and tiny llama.1
- Investigated novel quantization methods for optimizing LLMs including, AWQ, GPTQ, GGUF/GGML.2,5,6
- Developed a framework for LLM Smoothing, refining model weights using a modified version of OmniQuant that incorporates smoothing into the input of the down projection layer of the attention block and transitions from dynamic to static quantization.3,4
- Implemented Flash attention type tiling and an online normalization calculator for SoftMax to achieve memory-efficient precise attention mechanism on ARA NNPs.7,8
- Conducted analysis and pruning of LLM layers using Singular Value Decomposition and Block Importance methods to eliminate less important or redundant layers, thereby enhancing model memory bandwidth. Improved throughput from 2 Tokens/sec to 9 Tokens/sec with minimal decrease in accuracy on lm-eval.9,10
- Employed LoRA, QLoRA, and LoRA+ techniques to restore pruned models to achieve SOTA accuracy on lm-eval.11,12,13
- Established a Knowledge Distillation framework using PyTorch's FSDP method for distributed computing across multiple nodes and GPUs, utilizing NVIDIA's A10s, H100s, and A100 GPUs. This framework facilitates Knowledge distillation from a teacher model (e.g., Qwen7B or LLaMA7B) to a student model equipped with Quant and DeQuant (QDQ) stubs, supporting both static and dynamic quantization for QAT of the LLM model.14,15
References
[1] Dettmers, T., Lewis, M., Belkada, Y., & Zettlemoyer, L. (2022). "LLM.int8(): 8-bit Matrix Multiplication for Transformers at Scale." arXiv preprint arXiv:2208.07339. https://arxiv.org/pdf/2208.07339.pdf
[2] Lin, J., Tang, J., Tang, H., Yang, S., Dang, X., & Han, S. (2023). "AWQ: Activation-aware Weight Quantization for LLM Compression and Acceleration." arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.00978. https://arxiv.org/pdf/2306.00978.pdf
[3] Xiao, G., Lin, J., Seznec, M., Wu, H., Demouth, J., & Han, S. (2022). "SmoothQuant: Accurate and Efficient Post-Training Quantization for Large Language Models." arXiv preprint arXiv:2211.10438. https://arxiv.org/pdf/2211.10438.pdf
[4] Shao, W., Chen, M., Zhang, Z., Xu, P., Zhao, L., Li, Z., ... & Luo, P. (2023). "OmniQuant: Omnidirectionally Calibrated Quantization for Large Language Models." arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.13137. https://arxiv.org/abs/2308.13137
[5] Frantar, E., Ashkboos, S., Hoefler, T., & Alistarh, D. (2022). "GPTQ: Accurate Post-Training Quantization for Generative Pre-trained Transformers." arXiv preprint arXiv:2210.17323. https://arxiv.org/pdf/2210.17323.pdf
[6] Gerganov, G. (2023). "GGML: Tensor Library for Machine Learning." GitHub Repository. https://github.com/ggerganov/ggml
[7] Dao, T., Fu, D. Y., Ermon, S., Rudra, A., & Ré, C. (2022). "FlashAttention: Fast and Memory-Efficient Exact Attention with IO-Awareness." Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS). https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.14135
[8] Milakov, M., & Gimelshein, N. (2018). "Online Normalizer Calculation for Softmax." arXiv preprint arXiv:1805.02867. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1805.02867
[9] Gromov, A., Tirumala, K., Shapourian, H., Glorioso, P., & Roberts, D. A. (2024). "The Unreasonable Ineffectiveness of the Deeper Layers." arXiv preprint arXiv:2403.17887. https://arxiv.org/abs/2403.17887
[10] Sreenivas, S. T., Muralidharan, S., Joshi, R., Chochowski, M., Patwary, M., Shoeybi, M., ... & Korthikanti, V. (2024). "LLM Pruning and Distillation in Practice: The Minitron Approach." Mobius ML Blog. https://mobiusml.github.io/low-rank-llama2/
[11] Hu, E. J., Shen, Y., Wallis, P., Allen-Zhu, Z., Li, Y., Wang, S., ... & Chen, W. (2021). "LoRA: Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Language Models." arXiv preprint arXiv:2106.09685. https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.09685
[12] Dettmers, T., Pagnoni, A., Holtzman, A., & Zettlemoyer, L. (2023). "QLoRA: Efficient Finetuning of Quantized LLMs." Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS). https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.14314
[13] Hayou, S., Ghosh, N., & Yu, B. (2024). "LoRA+: Efficient Low Rank Adaptation of Large Models." arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.12354. https://arxiv.org/abs/2402.12354
[14] Liu, Z., Oguz, B., Zhao, C., Chang, E., Stock, P., Meber, Y., ... & Shi, W. (2023). "LLM-QAT: Data-Free Quantization Aware Training for Large Language Models." arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.17888. https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.17888
[15] Zhao, Y., Gu, A., Varma, R., Luo, L., Huang, C., Xu, M., ... & Ren, L. (2023). "PyTorch FSDP: Experiences on Scaling Fully Sharded Data Parallel." Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment, 16(12). https://arxiv.org/abs/2304.11277
-
2023Comparative Analysis of Rounding Techniques in Post Training Quantization for ResNet50 Model
I systematically explored the impact of different rounding techniques in post-training quantization, focusing on the ResNet50 model. The evaluated rounding methods include Rounding Away from Infinity (RAI), Round to Nearest Even (RNE), and Ada-round Simulator.
Results
Platform Model 2500 Image Set Accuracy Original PyTorch Model ResNet50 76.84% RAI ResNet50 74.00% RNE ResNet50 76.16% Ada-round Simulator ResNet50 76.84% References
Nagel, M., Amjad, R. A., Van Baalen, M., Louizos, C., & Blankevoort, T. (2020). "Up or Down? Adaptive Rounding for Post-Training Quantization." International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML). https://arxiv.org/pdf/2004.10568.pdf
Qualcomm AI Research. (2021). "AIMET: AI Model Efficiency Toolkit." MIT TinyML Lecture Series. https://hanlab.mit.edu/files/course/slides/MIT-TinyML-Lec25-AIMET.pdf
Qualcomm Innovation Center. (2023). "AIMET: AI Model Efficiency Toolkit." GitHub Repository. https://github.com/quic/aimet
Enhancing CLIP Model Performance through Transformer Block Analysis and Optimization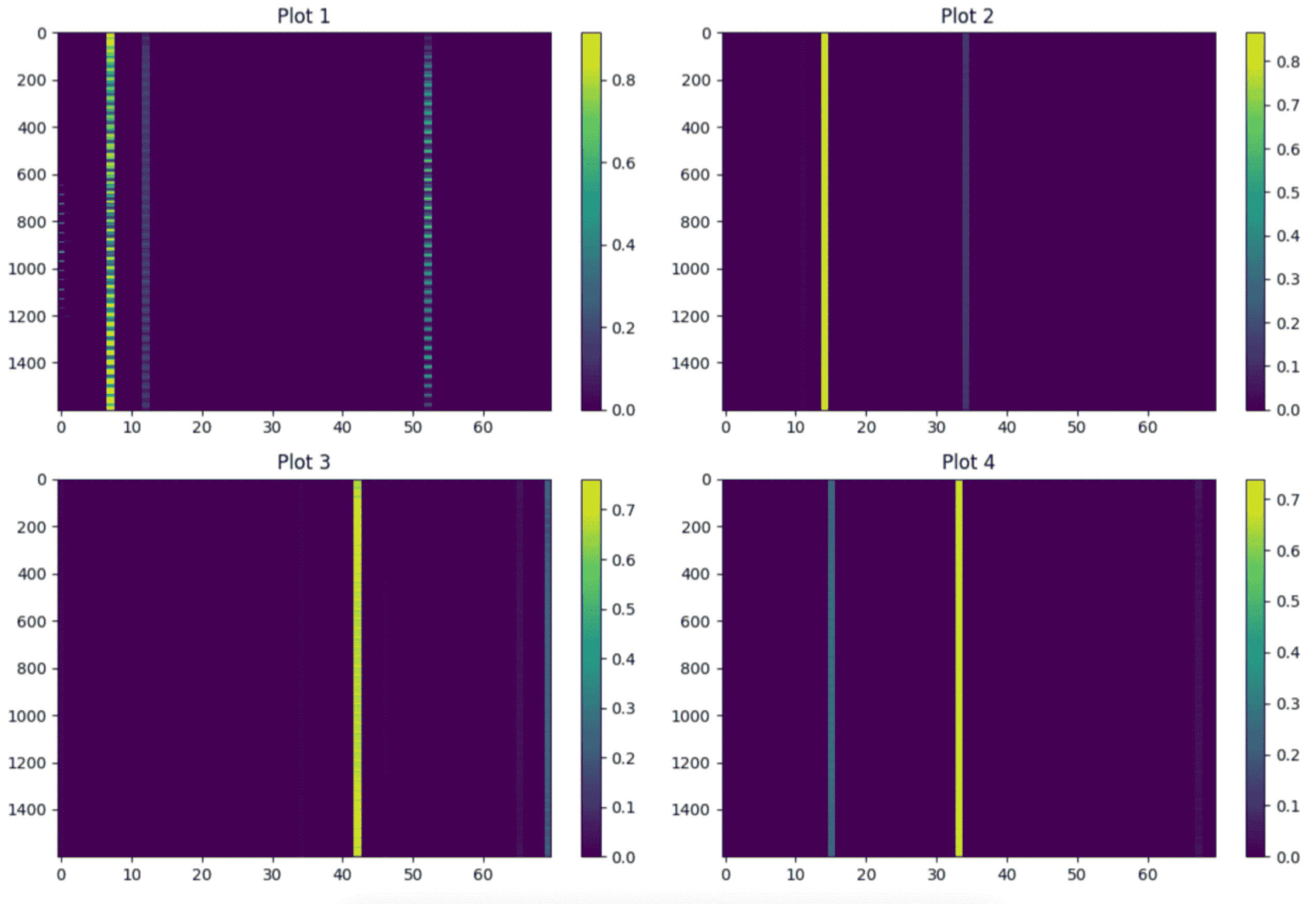
This work focused on optimizing OpenAI's CLIP model by enhancing its Transformer blocks, specifically focusing on the Key-Query-Value (KQV) projection layers through quantization observer analysis. The goal is to improve accuracy with minimal performance impact. Additionally, I investigated the impact of quantization errors in mean, variance, and inverse square root in Layer normalization within the Transformer block, proposing corrective measures for performance enhancement. Collaborating with Durga, we also analyzed systematic outliers in hidden layer features, developing a new quantization computation to mitigate errors arising from these outliers, as illustrated above.
References
Radford, A., Kim, J. W., Hallacy, C., Ramesh, A., Goh, G., Agarwal, S., ... & Sutskever, I. (2021). "Learning Transferable Visual Models From Natural Language Supervision." International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML). https://arxiv.org/pdf/2103.00020.pdf
Dettmers, T., Lewis, M., Belkada, Y., & Zettlemoyer, L. (2022). "LLM.int8(): 8-bit Matrix Multiplication for Transformers at Scale." arXiv preprint arXiv:2208.07339. https://arxiv.org/pdf/2208.07339.pdf
Impact of Observers on Rounding Techniques during Quantization Aware Training (QAT)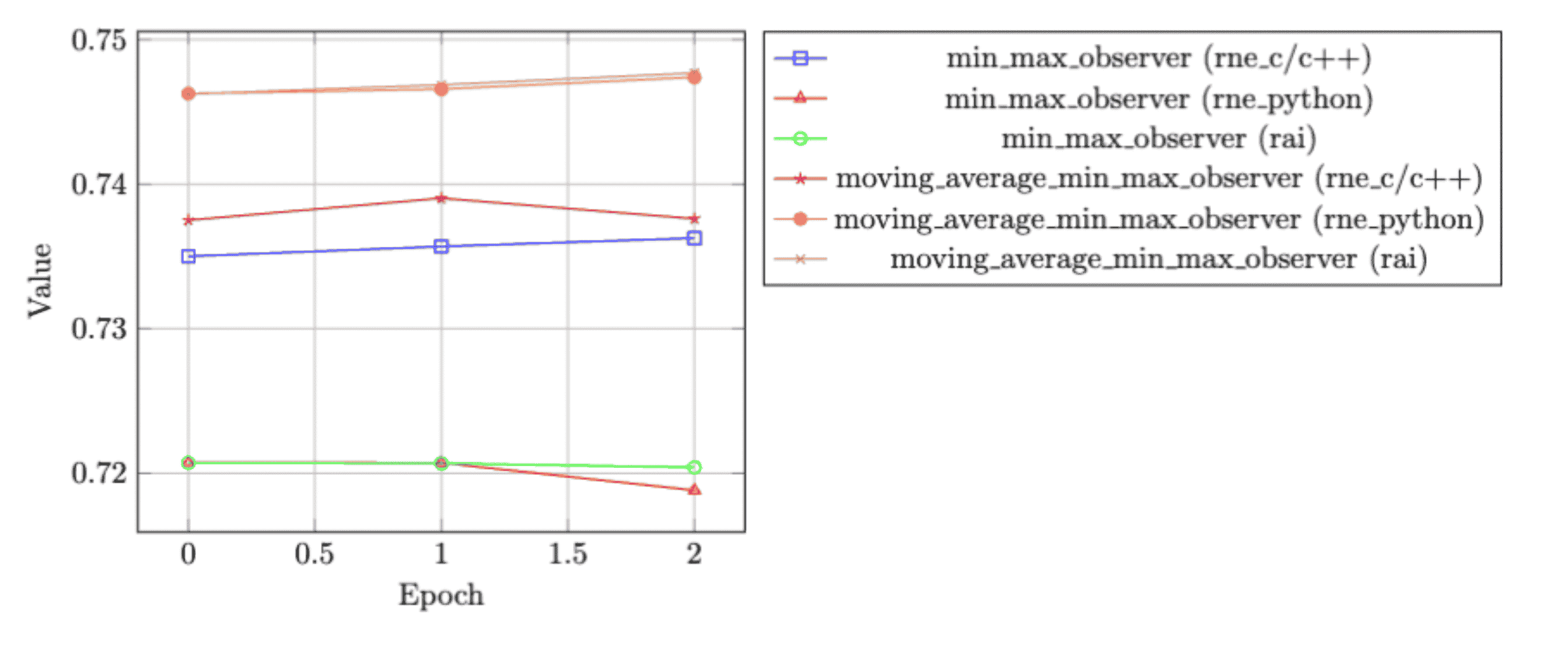
This research investigated the influence of different observers on the convergence behavior of quantization aware training (QAT) when coupled with various rounding techniques. The observers considered are
min_max_observerandmoving_average_min_max_observer, and the rounding techniques analyzed includerne_c/c++,rne_python, andrai. The evaluation is conducted across multiple epochs to understand the dynamics of convergence.Results
Observer Epoch RNE c/c++ RNE python RAI Min Max Observer 0 0.735 0.72074 0.72072 Min Max Observer 1 0.73568 0.72072 0.72068 Min Max Observer 2 0.73626 0.71882 0.7204 MA Min Max Observer 0 0.7375 0.746260 0.74622 MA Min Max Observer 1 0.73902 0.74656 0.74686 MA Min Max Observer 2 0.7376 0.74738 0.74768 References
PyTorch Team. (2023). "Quantization." PyTorch Documentation. https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/quantization.html
Mao, L. (2022). "PyTorch Quantization Aware Training." Lei Mao's Log Book. https://leimao.github.io/blog/PyTorch-Quantization-Aware-Training/
Advancements in Inverse Square Root Approximation for Neural Network Normalization Layers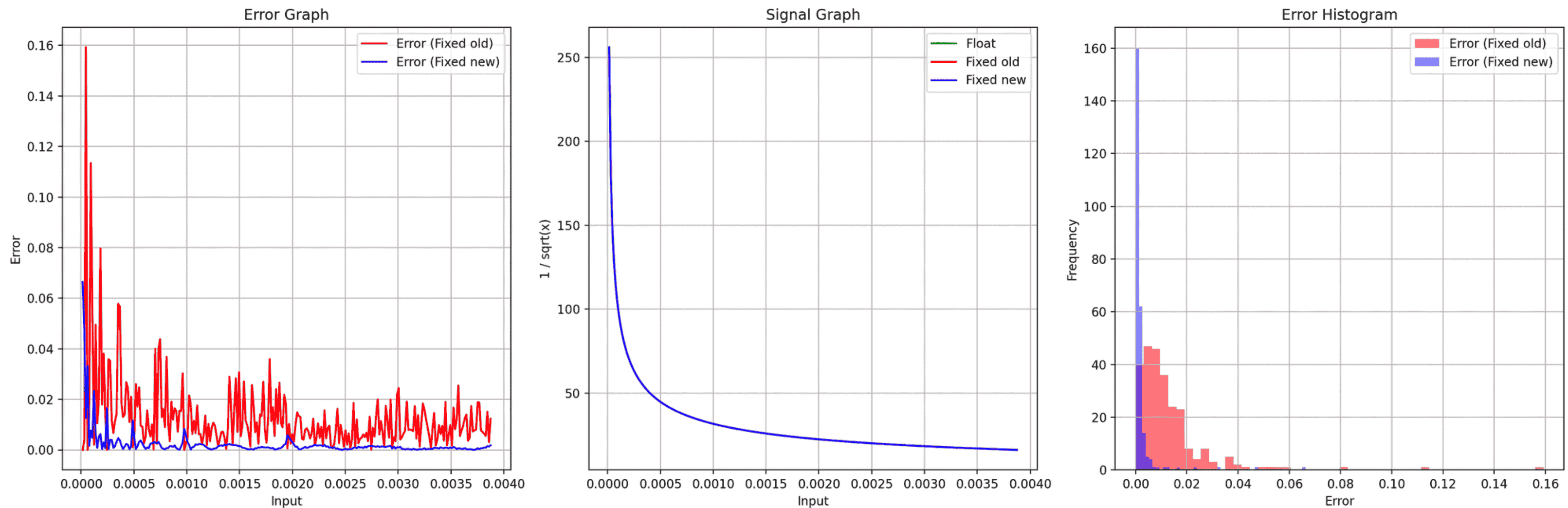
I developed an innovative function approximation for efficient ASIC processors, specifically targeting the inverse square root function. Our novel algorithm revolutionizes its application in normalization layers within neural networks, supporting both powers-of-two quantization and scale with zero-point quantization. Compared to existing techniques, our approximation is approximately 2x faster and exhibits a 30% improvement in accuracy. Evaluation metrics, including Mean Squared Error (MSE), Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR), and Mean Absolute Error (MAE), showcase significant advancements in both speed and precision.
Results
Metric Old Methods New Method % Improvement MSE 0.000404 0.000038 ~90.56% SNR (dB) 61.968707 72.234044 ~16.52% MAE 0.012692 0.002127 ~83.22% MSE % 0.000025% 0.000002% ~90.62% Max Error 0.159268 0.066406 ~58.36% Min Error 0.000000 0.000021 N/A Avg Error 0.012692 0.002127 ~83.22% The diagram above shows the old methods in red and the new method in blue.
The new algorithm's impact on transformer blocks, widely employed in diffusion models, LLMs, and image generation models like Stable Diffusion, is particularly noteworthy. The enhanced precision and computational efficiency contribute significantly to improving inference speeds in Language Models and facilitating the generation of high-quality images in models like Stable Diffusion.
-
2022Performance Enhancement through Swish Activation Analysis and Precision Optimization in YOLOv5 Models
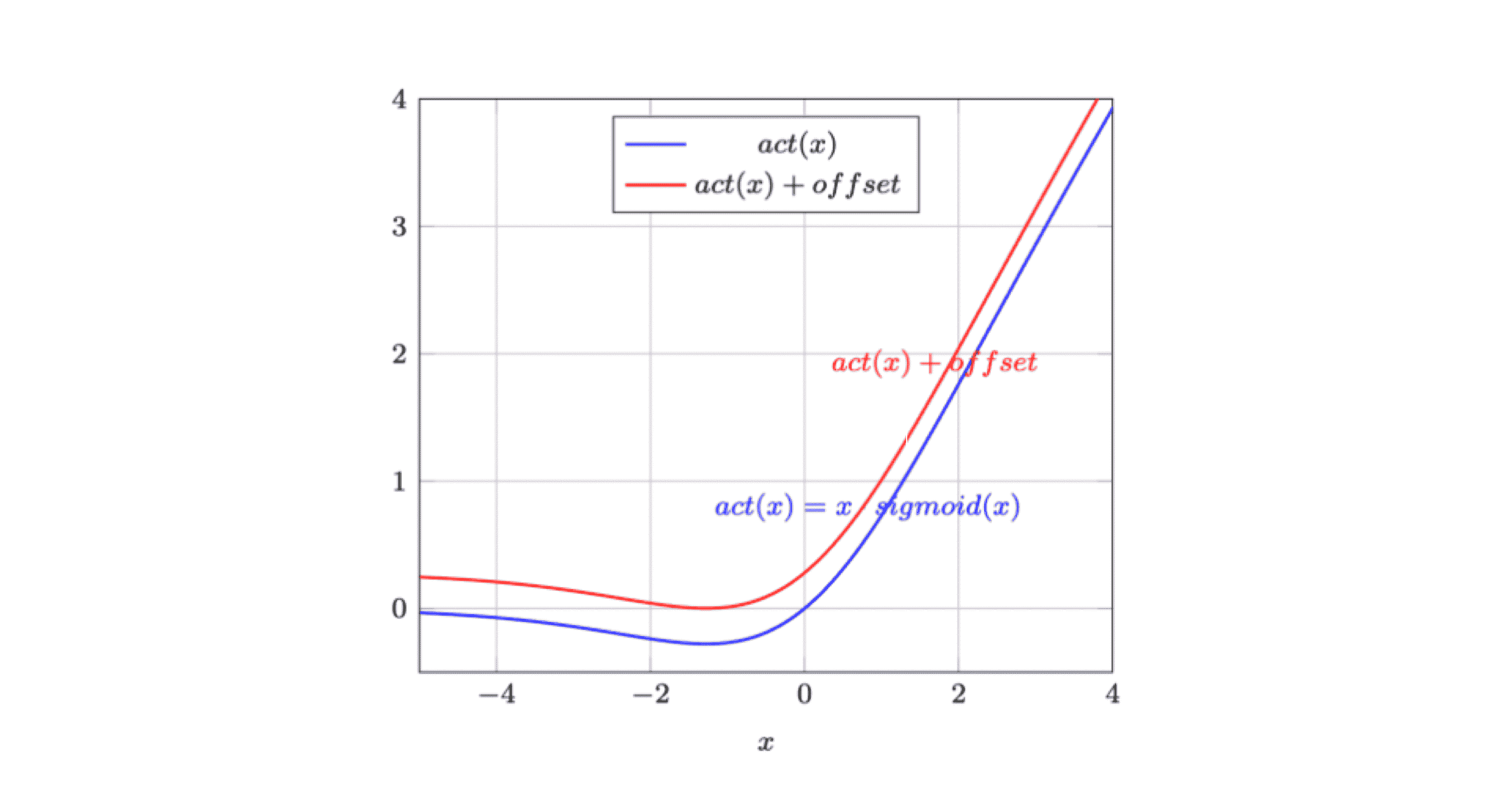
This work focused on optimizing YOLOv5 accuracy through activation distribution analysis. The quantized model, using Post-Training Quantization (PTQ) without Quantization-Aware Training (QAT), achieved improved precision by selectively offsetting activation functions to claim more bits for higher precision. Subsequent adjustments in the mathematical operations within the network compensated for the changes introduced in the activation layers.
Results
Model Configuration Average Precision (AP) @[IoU=0.50:0.95] Original float model 0.532 Quantized model with offset (PO2) 0.516 Quantized model without offset (PO2) 0.478 -
2021Designed the Math behind Precision-Preserving Kernels for Complex Mathematical Operations such as ROIAlign and Bilinear Interpolation on ASIC
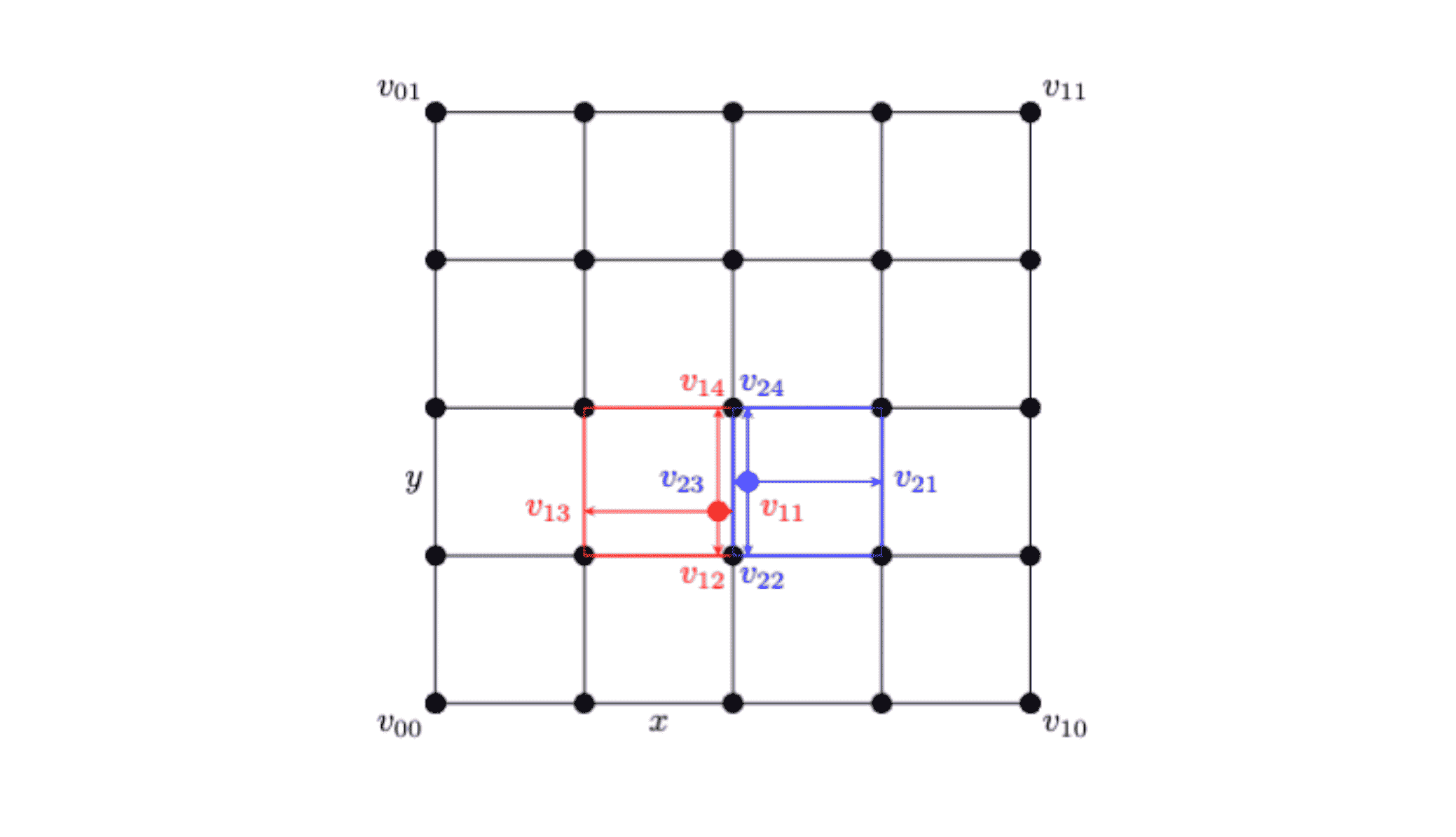
This research developed efficient int8 kernels and mathematical optimizations for the ROIAlign function. Custom ROIAlign kernels ensure accurate region-based feature extraction in computer vision. I addressed the challenges in bilinear interpolation due to quantization errors, emphasizing the importance of preserving precision. Small errors in quantization could result in significant shifts in bounding boxes (as shown in the figure above, where the red dot represented the actual FP32 point intended for the pixel within the red box, but quantization errors would shift the point to a new position as represented by the blue dot, resulting in the selection of the pixel represented by the blue rectangle). This shift caused high errors in the bounding boxes, ultimately resulting in incorrect object detections in YOLO models. I successfully navigated this challenge, achieving a quantization strategy that struck a delicate balance between computational efficiency and precision.
References
He, K., Gkioxari, G., Dollár, P., & Girshick, R. (2017). "Mask R-CNN." IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). https://paperswithcode.com/method/roi-align
-
2020Kernel Development for Efficient Powers-of-Two Approximation Exponentiation and Application to SoftMax Function
This research introduced a novel kernel designed for accurate powers-of-two approximation exponentiation. Leveraging polynomial fitting and the Newton-Raphson method, our approach (along with Aditya) optimized the computation of exponentiation, offering a balance between precision and efficiency. The kernel's versatility extends beyond traditional exponentiation applications to include the SoftMax function.
ex = 2(x/ln(2))
- Precalculate 1/ln(2)
- Multiply this constant by your argument (1 multiplication)
- Use binary shifts to raise 2 to the integer portion of the power (assumes exp+mantissa format)
- Approximate and quantize the fractional part.
- Adjust based on the fractional power-of-2 remainder (likely a second multiplication)
References
Muller, J. M. (2006). "Elementary Functions: Algorithms and Implementation." Birkhäuser Boston. See also: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/6984440/approximate-ex
-
2019Convolutional Neural Networks based Dementia and Tumor Classification from MRI Brain Images
Under the guidance of Prof. N. Ruban at VIT Vellore. Published in IEEE Xplore at CICT Conference.